- Mozambique
-
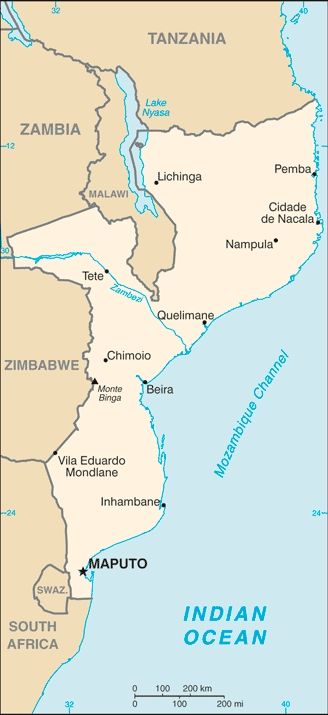 Introduction ::MozambiqueBackground:Almost five centuries as a Portuguese colony came to a close with independence in 1975. Large-scale emigration, economic dependence on South Africa, a severe drought, and a prolonged civil war hindered the country's development until the mid 1990s. The ruling Front for the Liberation of Mozambique (Frelimo) party formally abandoned Marxism in 1989, and a new constitution the following year provided for multiparty elections and a free market economy. A UN-negotiated peace agreement between Frelimo and rebel Mozambique National Resistance (Renamo) forces ended the fighting in 1992. In December 2004, Mozambique underwent a delicate transition as Joaquim CHISSANO stepped down after 18 years in office. His elected successor, Armando Emilio GUEBUZA, promised to continue the sound economic policies that have encouraged foreign investment. President GUEBUZA was reelected to a second term in October 2009. However, the elections were flawed by voter fraud, questionable disqualification of candidates, and Frelimo use of government resources during the campaign. As a result, Freedom House removed Mozambique from its list of electoral democracies.Geography ::MozambiqueLocation:Southeastern Africa, bordering the Mozambique Channel, between South Africa and TanzaniaGeographic coordinates:18 15 S, 35 00 EArea:total: 799,380 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 35land: 786,380 sq kmwater: 13,000 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly less than twice the size of CaliforniaLand boundaries:total: 4,571 kmborder countries: Malawi 1,569 km, South Africa 491 km, Swaziland 105 km, Tanzania 756 km, Zambia 419 km, Zimbabwe 1,231 kmCoastline:2,470 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmClimate:tropical to subtropicalTerrain:mostly coastal lowlands, uplands in center, high plateaus in northwest, mountains in westElevation extremes:lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 mhighest point: Monte Binga 2,436 mNatural resources:coal, titanium, natural gas, hydropower, tantalum, graphiteLand use:arable land: 6.51%permanent crops: 0.25%other: 93.24% (2011)Irrigated land:1,181 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:217.1 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 0.88 cu km/yr (26%/4%/70%)per capita: 46.05 cu m/yr (2005)Natural hazards:severe droughts; devastating cyclones and floods in central and southern provincesEnvironment - current issues:a long civil war and recurrent drought in the hinterlands have resulted in increased migration of the population to urban and coastal areas with adverse environmental consequences; desertification; pollution of surface and coastal waters; elephant poaching for ivory is a problemEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:the Zambezi flows through the north-central and most fertile part of the countryPeople and Society ::MozambiqueNationality:noun: Mozambican(s)adjective: MozambicanEthnic groups:African 99.66% (Makhuwa, Tsonga, Lomwe, Sena, and others), Europeans 0.06%, Euro-Africans 0.2%, Indians 0.08%Languages:Emakhuwa 25.3%, Portuguese (official) 10.7%, Xichangana 10.3%, Cisena 7.5%, Elomwe 7%, Echuwabo 5.1%, other Mozambican languages 30.1%, other 4% (1997 census)Religions:Catholic 28.4%, Protestant 27.7% (Zionist Christian 15.5%, Evangelical Pentecostal 10.9%, Anglican 1.3%), Muslim 17.9%, other 7.2%, none 18.7% (1997 census)Population:24,096,669 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 50note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expectedAge structure:0-14 years: 45.5% (male 5,515,341/female 5,457,336)15-24 years: 21.1% (male 2,469,221/female 2,610,720)25-54 years: 27% (male 3,035,069/female 3,461,519)55-64 years: 3.5% (male 396,186/female 442,237)65 years and over: 2.9% (male 325,955/female 383,085) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 94.8 %youth dependency ratio: 88.4 %elderly dependency ratio: 6.4 %potential support ratio: 15.6 (2013)Median age:total: 16.8 yearsmale: 16.2 yearsfemale: 17.5 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:2.44% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 33Birth rate:39.08 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 11Death rate:12.57 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Net migration rate:-2.07 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 164Urbanization:urban population: 31.2% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 3.05% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:MAPUTO (capital) 1.589 million; Matola 761,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.02 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.93 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.88 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.89 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:18.8 (2003 est.)Maternal mortality rate:490 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 20Infant mortality rate:total: 74.63 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 13male: 76.78 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 72.43 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 52.29 yearscountry comparison to the world: 213male: 51.54 yearsfemale: 53.06 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:5.34 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 12Contraceptive prevalence rate:11.6% (2011)Health expenditures:5.2% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 128Physicians density:0.03 physicians/1,000 population (2006)Hospital bed density:0.7 beds/1,000 population (2011)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 77% of populationrural: 29% of populationtotal: 47% of populationunimproved:urban: 23% of populationrural: 71% of populationtotal: 53% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 38% of populationrural: 5% of populationtotal: 18% of populationunimproved:urban: 62% of populationrural: 95% of populationtotal: 82% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:11.5% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 8HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:1.4 million (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 5HIV/AIDS - deaths:74,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: very highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue feverwater contact disease: schistosomiasisanimal contact disease: rabies (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:4.9% (2008)country comparison to the world: 158Children under the age of 5 years underweight:18.3% (2008)country comparison to the world: 39Education expenditures:5% of GDP (2006)country comparison to the world: 76Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 56.1%male: 70.8%female: 42.8% (2010 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 10 yearsmale: 10 yearsfemale: 9 years (2011)Child labor - children ages 5-14:total number: 1,369,080percentage: 22 % (2008 est.)Government ::MozambiqueCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Mozambiqueconventional short form: Mozambiquelocal long form: Republica de Mocambiquelocal short form: Mocambiqueformer: Portuguese East AfricaGovernment type:republicCapital:name: Maputogeographic coordinates: 25 57 S, 32 35 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:10 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia), 1 city (cidade)*; Cabo Delgado, Gaza, Inhambane, Manica, Maputo, Cidade de Maputo*, Nampula, Niassa, Sofala, Tete, ZambeziaIndependence:25 June 1975 (from Portugal)National holiday:Independence Day, 25 June (1975)Constitution:30 November 1990Legal system:mixed legal system of Portuguese civil law, Islamic law, and customary lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Armando Emilio GUEBUZA (since 2 February 2005)head of government: Prime Minister Alberto Clementino VAQUINA (since 8 October 2012)cabinet: Cabinet(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for three terms); election last held on 28 October 2009 (next to be held in 2014); prime minister appointed by the presidentelection results: Armando GUEBUZA reelected president; percent of vote - Armando GUEBUZA 76.3%, Afonso DHLAKAMA 14.9%, Daviz SIMANGO 8.8%Legislative branch:unicameral Assembly of the Republic or Assembleia da Republica (250 seats; members directly elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)elections: last held on 28 October 2009 (next to be held in 2014)election results: percent of vote by party - FRELIMO 74.7%, RENAMO 17.7%, MDM 3.9%, other 3.7%; seats by party - FRELIMO 191, RENAMO 51, MDM 8Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the court president, vice president, and 5 judges); Constitutional Council (consists of 7 judges)note - the Higher Council of the Judiciary is responsible for judiciary management and disciplinejudge selection and term of office: Supreme Court president and vice president appointed by Mozambique president in consultation with the Higher Council of the Judiciary (CSMJ) and with ratification by the legislature; other judges elected by the legislature; judges serve 5-year renewable terms; Constitutional Council judges appointed - 1 by the president, 5 by the legislature, and 1 by the CSMJ; judges serve 5-year nonrenewable termssubordinate courts: Administrative Court (capital city only); provincial courts or Tribunais Judicias de Provincia; District Courts or Tribunais Judicias de Districto; customs courts; maritime courts; courts marshal; labor courts; community courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Democratic Movement of Mozambique (Movimento Democratico de Mocambique) or MDM [Daviz SIMANGO]Front for the Liberation of Mozambique (Frente de Liberatacao de Mocambique) or FRELIMO [Armando Emilio GUEBUZA]Mozambique National Resistance (Resistencia Nacional Mocambicana) or RENAMO [Afonso DHLAKAMA]Political pressure groups and leaders:Mozambican League of Human Rights (Liga Mocambicana dos Direitos Humanos) or LDH [Alice MABOTE, president]International organization participation:ACP, AfDB, AU, C, CD, CPLP, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OIC, OIF (observer), OPCW, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNISFA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Amelia Matos SUMBANAchancery: 1525 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036telephone: [1] (202) 293-7146FAX: [1] (202) 835-0245Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Douglas M. GRIFFITHSembassy: Avenida Kenneth Kuanda 193, Maputomailing address: P. O. Box 783, Maputotelephone: [258] (21) 492797FAX: [258] (21) 490114Flag description:three equal horizontal bands of green (top), black, and yellow with a red isosceles triangle based on the hoist side; the black band is edged in white; centered in the triangle is a yellow five-pointed star bearing a crossed rifle and hoe in black superimposed on an open white book; green represents the riches of the land, white peace, black the African continent, yellow the country's minerals, and red the struggle for independence; the rifle symbolizes defense and vigilance, the hoe refers to the country's agriculture, the open book stresses the importance of education, and the star represents Marxism and internationalismNational anthem:name: ""Patria Amada"" (Lovely Fatherland)lyrics/music: Salomao J. MANHICA/unknownnote: adopted 2002Economy ::MozambiqueEconomy - overview:At independence in 1975, Mozambique was one of the world's poorest countries. Socialist mismanagement and a brutal civil war from 1977-92 exacerbated the situation. In 1987, the government embarked on a series of macroeconomic reforms designed to stabilize the economy. These steps, combined with donor assistance and with political stability since the multi-party elections in 1994, have led to dramatic improvements in the country's growth rate. Fiscal reforms, including the introduction of a value-added tax and reform of the customs service, have improved the government's revenue collection abilities. In spite of these gains, Mozambique remained dependent upon foreign assistance for 40% of its 2012 annual budget and over half the population remained below the poverty line. Subsistence agriculture continues to employ the vast majority of the country's work force and smallholder agricultural productivity and productivity growth is weak. A substantial trade imbalance persists although aluminum production from the Mozal smelter has significantly boosted export earnings in recent years. In 2012, The Mozambican government took over Portugal's last remaining share in the Cahora Bassa Hydroelectricity Company (HCB), a signficant contributor to the Southern African Power Pool. The government has plans to expand the Cahora Bassa Dam and build additional dams to increase its electricity exports and fulfill the needs of its burgeoning domestic industries. Mozambique's once substantial foreign debt has been reduced through forgiveness and rescheduling under the IMF's Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) and Enhanced HIPC initiatives, and is now at a manageable level. In July 2007, the US government's Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC) signed a $506.9 million Compact with Mozambique. Compact projects will end in September 2013 and are focusing on improving sanitation, roads, agriculture, and the business regulation environment in an effort to spur economic growth in the four northern provinces of the country. Citizens rioted in September 2010, after fuel, water, electricity, and bread price increases were announced. In an attempt to lessen the negative impact on people, the government implemented subsidies, decreased taxes and tariffs, and instituted other fiscal measures. Mozambique grew at an average annual rate of 6%-8% in the decade up to 2012, one of Africa's strongest performances. Mozambique's ability to attract large investment projects in natural resources is expected to fuel continued high growth in coming years. Revenues from these vast resources, including natural gas, coal, titanium and hydroelectric capacity, could overtake donor assistance within five years.GDP (purchasing power parity):$26.69 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 119$24.83 billion (2011 est.)$23.13 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$14.6 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:7.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 237.3% (2011 est.)7.1% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$1,200 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 210$1,100 (2011 est.)$1,100 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:0% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1425.2% of GDP (2011 est.)4.8% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 77.3%government consumption: 13.5%investment in fixed capital: 24.8%investment in inventories: 0.9%exports of goods and services: 27%imports of goods and services: -43.8%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 29.5%industry: 23.9%services: 46.5% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:cotton, cashew nuts, sugarcane, tea, cassava (tapioca), corn, coconuts, sisal, citrus and tropical fruits, potatoes, sunflowers; beef, poultryIndustries:aluminum, petroleum products, chemicals (fertilizer, soap, paints), textiles, cement, glass, asbestos, tobacco, food, beveragesIndustrial production growth rate:12% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 6Labor force:10.1 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 81%industry: 6%services: 13% (1997 est.)Unemployment rate:17% (2007 est.)country comparison to the world: 15221% (1997 est.)Population below poverty line:52% (2009 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 1.9%highest 10%: 36.7% (2008)Distribution of family income - Gini index:45.6 (2008)country comparison to the world: 3747.3 (2002)Budget:revenues: $4.315 billionexpenditures: $4.904 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:29.6% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 94Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-4% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 142Public debt:34.6% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 10634.5% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):2.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 4310.4% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:9.5% (17 January 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1003.25% (31 December 2010 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:16.81% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1819.1% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$4.335 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 102$3.574 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$5.268 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 128$4.095 billion (31 December 2010 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$3.9 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 126$3.392 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$NACurrent account balance:-$2.432 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 144-$1.615 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$3.469 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 126$3.118 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:aluminum, prawns, cashews, cotton, sugar, citrus, timber; bulk electricityExports - partners:South Africa 30.9%, Belgium 12.8%, China 9%, Italy 7.8%, Spain 6.2%, India 5.6% (2012)Imports:$6.167 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 120$5.368 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and equipment, vehicles, fuel, chemicals, metal products, foodstuffs, textilesImports - partners:South Africa 30.7%, China 12.2%, India 11.4%, US 5.1%, Portugal 4.8%, Australia 4.4% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$2.77 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 113$2.469 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$4.562 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 122$4.097 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:meticais (MZM) per US dollar -28.383 (2012 est.)29.075 (2011 est.)33.96 (2010 est.)26.28 (2009)24.125 (2008)Energy ::MozambiqueElectricity - production:14.83 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Electricity - consumption:10.19 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Electricity - exports:9.462 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 21Electricity - imports:8.537 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Electricity - installed generating capacity:2.28 million kW (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 98Electricity - from fossil fuels:0.1% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 206Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:99.9% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Electricity - from other renewable sources:0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 163Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 169Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 156Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 102Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 210Refined petroleum products - consumption:19,580 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 128Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 204Refined petroleum products - imports:13,200 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 123Natural gas - production:3.12 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 54Natural gas - consumption:80 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 107Natural gas - exports:3.04 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 101Natural gas - proved reserves:127.4 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 51Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:2.728 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 143Communications ::MozambiqueTelephones - main lines in use:88,100 (2011)country comparison to the world: 147Telephones - mobile cellular:7.855 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 89Telephone system:general assessment: a fair telecommunications system that is shackled with a heavy state presence, lack of competition, and high operating costs and chargesdomestic: stagnation in the fixed-line network contrasts with rapid growth in the mobile-cellular network; mobile-cellular coverage now includes all the main cities and key roads, including those from Maputo to the South African and Swaziland borders, the national highway through Gaza and Inhambane provinces, the Beira corridor, and from Nampula to Nacala; extremely low fixed-line teledensity; despite significant growth in mobile-cellular services, teledensity remains low at about 35 per 100 personsinternational: country code - 258; landing point for the EASSy and SEACOM fiber-optic submarine cable systems; satellite earth stations - 5 Intelsat (2 Atlantic Ocean and 3 Indian Ocean) (2011)Broadcast media:1 state-run TV station supplemented by private TV station; Portuguese state TV's African service, RTP Africa, and Brazilian-owned TV Miramar are available; state-run radio provides nearly 100% territorial coverage and broadcasts in multiple languages; a number of privately owned and community-operated stations; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters are available (2007)Internet country code:.mzInternet hosts:89,737 (2012)country comparison to the world: 82Internet users:613,600 (2009)country comparison to the world: 113Transportation ::MozambiqueAirports:98 (2013)country comparison to the world: 57Airports - with paved runways:total: 21over 3,047 m: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 9914 to 1,523 m: 5under 914 m: 4 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 772,438 to 3,047 m: 11,524 to 2,437 m: 9914 to 1,523 m: 29under 914 m:38 (2013)Pipelines:gas 972 km; refined products 278 km (2013)Railways:total: 4,787 kmcountry comparison to the world: 38narrow gauge: 4,787 km 1.067-m gauge (2008)Roadways:total: 30,331 kmcountry comparison to the world: 96paved: 6,303 kmunpaved: 24,028 km (2000)Waterways:460 km (Zambezi River navigable to Tete and along Cahora Bassa Lake) (2010)country comparison to the world: 86Merchant marine:total: 2country comparison to the world: 143by type: cargo 2foreign-owned: 2 (Belgium 2) (2010)Ports and terminals:Beira, Maputo, NacalaMilitary ::MozambiqueMilitary branches:Mozambique Armed Defense Forces (Forcas Armadas de Defesa de Mocambique, FADM): Mozambique Army, Mozambique Navy (Marinha de Guerra de Mocambique, MGM), Mozambique Air Force (Forca Aerea de Mocambique, FAM) (2012)Military service age and obligation:registration for military service is mandatory for all males and females at 18 years of age; 18-35 years of age for selective compulsory military service; 18 years of age for voluntary service; 2-year service obligation; women may serve as officers or enlisted (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 4,613,367 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 2,677,473females age 16-49: 2,941,073 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 274,602female: 280,008 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:0.6% of GDP (2012)country comparison to the world: 158Transnational Issues ::MozambiqueDisputes - international:South Africa has placed military units to assist police operations along the border of Lesotho, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique to control smuggling, poaching, and illegal migrationIllicit drugs:southern African transit point for South Asian hashish and heroin, and South American cocaine probably destined for the European and South African markets; producer of cannabis (for local consumption) and methaqualone (for export to South Africa); corruption and poor regulatory capability make the banking system vulnerable to money laundering, but the lack of a well-developed financial infrastructure limits the country's utility as a money-laundering center"
Introduction ::MozambiqueBackground:Almost five centuries as a Portuguese colony came to a close with independence in 1975. Large-scale emigration, economic dependence on South Africa, a severe drought, and a prolonged civil war hindered the country's development until the mid 1990s. The ruling Front for the Liberation of Mozambique (Frelimo) party formally abandoned Marxism in 1989, and a new constitution the following year provided for multiparty elections and a free market economy. A UN-negotiated peace agreement between Frelimo and rebel Mozambique National Resistance (Renamo) forces ended the fighting in 1992. In December 2004, Mozambique underwent a delicate transition as Joaquim CHISSANO stepped down after 18 years in office. His elected successor, Armando Emilio GUEBUZA, promised to continue the sound economic policies that have encouraged foreign investment. President GUEBUZA was reelected to a second term in October 2009. However, the elections were flawed by voter fraud, questionable disqualification of candidates, and Frelimo use of government resources during the campaign. As a result, Freedom House removed Mozambique from its list of electoral democracies.Geography ::MozambiqueLocation:Southeastern Africa, bordering the Mozambique Channel, between South Africa and TanzaniaGeographic coordinates:18 15 S, 35 00 EArea:total: 799,380 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 35land: 786,380 sq kmwater: 13,000 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly less than twice the size of CaliforniaLand boundaries:total: 4,571 kmborder countries: Malawi 1,569 km, South Africa 491 km, Swaziland 105 km, Tanzania 756 km, Zambia 419 km, Zimbabwe 1,231 kmCoastline:2,470 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmClimate:tropical to subtropicalTerrain:mostly coastal lowlands, uplands in center, high plateaus in northwest, mountains in westElevation extremes:lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 mhighest point: Monte Binga 2,436 mNatural resources:coal, titanium, natural gas, hydropower, tantalum, graphiteLand use:arable land: 6.51%permanent crops: 0.25%other: 93.24% (2011)Irrigated land:1,181 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:217.1 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 0.88 cu km/yr (26%/4%/70%)per capita: 46.05 cu m/yr (2005)Natural hazards:severe droughts; devastating cyclones and floods in central and southern provincesEnvironment - current issues:a long civil war and recurrent drought in the hinterlands have resulted in increased migration of the population to urban and coastal areas with adverse environmental consequences; desertification; pollution of surface and coastal waters; elephant poaching for ivory is a problemEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:the Zambezi flows through the north-central and most fertile part of the countryPeople and Society ::MozambiqueNationality:noun: Mozambican(s)adjective: MozambicanEthnic groups:African 99.66% (Makhuwa, Tsonga, Lomwe, Sena, and others), Europeans 0.06%, Euro-Africans 0.2%, Indians 0.08%Languages:Emakhuwa 25.3%, Portuguese (official) 10.7%, Xichangana 10.3%, Cisena 7.5%, Elomwe 7%, Echuwabo 5.1%, other Mozambican languages 30.1%, other 4% (1997 census)Religions:Catholic 28.4%, Protestant 27.7% (Zionist Christian 15.5%, Evangelical Pentecostal 10.9%, Anglican 1.3%), Muslim 17.9%, other 7.2%, none 18.7% (1997 census)Population:24,096,669 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 50note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expectedAge structure:0-14 years: 45.5% (male 5,515,341/female 5,457,336)15-24 years: 21.1% (male 2,469,221/female 2,610,720)25-54 years: 27% (male 3,035,069/female 3,461,519)55-64 years: 3.5% (male 396,186/female 442,237)65 years and over: 2.9% (male 325,955/female 383,085) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 94.8 %youth dependency ratio: 88.4 %elderly dependency ratio: 6.4 %potential support ratio: 15.6 (2013)Median age:total: 16.8 yearsmale: 16.2 yearsfemale: 17.5 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:2.44% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 33Birth rate:39.08 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 11Death rate:12.57 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Net migration rate:-2.07 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 164Urbanization:urban population: 31.2% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 3.05% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:MAPUTO (capital) 1.589 million; Matola 761,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.02 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.93 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.88 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.89 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:18.8 (2003 est.)Maternal mortality rate:490 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 20Infant mortality rate:total: 74.63 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 13male: 76.78 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 72.43 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 52.29 yearscountry comparison to the world: 213male: 51.54 yearsfemale: 53.06 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:5.34 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 12Contraceptive prevalence rate:11.6% (2011)Health expenditures:5.2% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 128Physicians density:0.03 physicians/1,000 population (2006)Hospital bed density:0.7 beds/1,000 population (2011)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 77% of populationrural: 29% of populationtotal: 47% of populationunimproved:urban: 23% of populationrural: 71% of populationtotal: 53% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 38% of populationrural: 5% of populationtotal: 18% of populationunimproved:urban: 62% of populationrural: 95% of populationtotal: 82% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:11.5% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 8HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:1.4 million (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 5HIV/AIDS - deaths:74,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: very highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue feverwater contact disease: schistosomiasisanimal contact disease: rabies (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:4.9% (2008)country comparison to the world: 158Children under the age of 5 years underweight:18.3% (2008)country comparison to the world: 39Education expenditures:5% of GDP (2006)country comparison to the world: 76Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 56.1%male: 70.8%female: 42.8% (2010 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 10 yearsmale: 10 yearsfemale: 9 years (2011)Child labor - children ages 5-14:total number: 1,369,080percentage: 22 % (2008 est.)Government ::MozambiqueCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Mozambiqueconventional short form: Mozambiquelocal long form: Republica de Mocambiquelocal short form: Mocambiqueformer: Portuguese East AfricaGovernment type:republicCapital:name: Maputogeographic coordinates: 25 57 S, 32 35 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:10 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia), 1 city (cidade)*; Cabo Delgado, Gaza, Inhambane, Manica, Maputo, Cidade de Maputo*, Nampula, Niassa, Sofala, Tete, ZambeziaIndependence:25 June 1975 (from Portugal)National holiday:Independence Day, 25 June (1975)Constitution:30 November 1990Legal system:mixed legal system of Portuguese civil law, Islamic law, and customary lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Armando Emilio GUEBUZA (since 2 February 2005)head of government: Prime Minister Alberto Clementino VAQUINA (since 8 October 2012)cabinet: Cabinet(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for three terms); election last held on 28 October 2009 (next to be held in 2014); prime minister appointed by the presidentelection results: Armando GUEBUZA reelected president; percent of vote - Armando GUEBUZA 76.3%, Afonso DHLAKAMA 14.9%, Daviz SIMANGO 8.8%Legislative branch:unicameral Assembly of the Republic or Assembleia da Republica (250 seats; members directly elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)elections: last held on 28 October 2009 (next to be held in 2014)election results: percent of vote by party - FRELIMO 74.7%, RENAMO 17.7%, MDM 3.9%, other 3.7%; seats by party - FRELIMO 191, RENAMO 51, MDM 8Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the court president, vice president, and 5 judges); Constitutional Council (consists of 7 judges)note - the Higher Council of the Judiciary is responsible for judiciary management and disciplinejudge selection and term of office: Supreme Court president and vice president appointed by Mozambique president in consultation with the Higher Council of the Judiciary (CSMJ) and with ratification by the legislature; other judges elected by the legislature; judges serve 5-year renewable terms; Constitutional Council judges appointed - 1 by the president, 5 by the legislature, and 1 by the CSMJ; judges serve 5-year nonrenewable termssubordinate courts: Administrative Court (capital city only); provincial courts or Tribunais Judicias de Provincia; District Courts or Tribunais Judicias de Districto; customs courts; maritime courts; courts marshal; labor courts; community courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Democratic Movement of Mozambique (Movimento Democratico de Mocambique) or MDM [Daviz SIMANGO]Front for the Liberation of Mozambique (Frente de Liberatacao de Mocambique) or FRELIMO [Armando Emilio GUEBUZA]Mozambique National Resistance (Resistencia Nacional Mocambicana) or RENAMO [Afonso DHLAKAMA]Political pressure groups and leaders:Mozambican League of Human Rights (Liga Mocambicana dos Direitos Humanos) or LDH [Alice MABOTE, president]International organization participation:ACP, AfDB, AU, C, CD, CPLP, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OIC, OIF (observer), OPCW, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNISFA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Amelia Matos SUMBANAchancery: 1525 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036telephone: [1] (202) 293-7146FAX: [1] (202) 835-0245Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Douglas M. GRIFFITHSembassy: Avenida Kenneth Kuanda 193, Maputomailing address: P. O. Box 783, Maputotelephone: [258] (21) 492797FAX: [258] (21) 490114Flag description:three equal horizontal bands of green (top), black, and yellow with a red isosceles triangle based on the hoist side; the black band is edged in white; centered in the triangle is a yellow five-pointed star bearing a crossed rifle and hoe in black superimposed on an open white book; green represents the riches of the land, white peace, black the African continent, yellow the country's minerals, and red the struggle for independence; the rifle symbolizes defense and vigilance, the hoe refers to the country's agriculture, the open book stresses the importance of education, and the star represents Marxism and internationalismNational anthem:name: ""Patria Amada"" (Lovely Fatherland)lyrics/music: Salomao J. MANHICA/unknownnote: adopted 2002Economy ::MozambiqueEconomy - overview:At independence in 1975, Mozambique was one of the world's poorest countries. Socialist mismanagement and a brutal civil war from 1977-92 exacerbated the situation. In 1987, the government embarked on a series of macroeconomic reforms designed to stabilize the economy. These steps, combined with donor assistance and with political stability since the multi-party elections in 1994, have led to dramatic improvements in the country's growth rate. Fiscal reforms, including the introduction of a value-added tax and reform of the customs service, have improved the government's revenue collection abilities. In spite of these gains, Mozambique remained dependent upon foreign assistance for 40% of its 2012 annual budget and over half the population remained below the poverty line. Subsistence agriculture continues to employ the vast majority of the country's work force and smallholder agricultural productivity and productivity growth is weak. A substantial trade imbalance persists although aluminum production from the Mozal smelter has significantly boosted export earnings in recent years. In 2012, The Mozambican government took over Portugal's last remaining share in the Cahora Bassa Hydroelectricity Company (HCB), a signficant contributor to the Southern African Power Pool. The government has plans to expand the Cahora Bassa Dam and build additional dams to increase its electricity exports and fulfill the needs of its burgeoning domestic industries. Mozambique's once substantial foreign debt has been reduced through forgiveness and rescheduling under the IMF's Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) and Enhanced HIPC initiatives, and is now at a manageable level. In July 2007, the US government's Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC) signed a $506.9 million Compact with Mozambique. Compact projects will end in September 2013 and are focusing on improving sanitation, roads, agriculture, and the business regulation environment in an effort to spur economic growth in the four northern provinces of the country. Citizens rioted in September 2010, after fuel, water, electricity, and bread price increases were announced. In an attempt to lessen the negative impact on people, the government implemented subsidies, decreased taxes and tariffs, and instituted other fiscal measures. Mozambique grew at an average annual rate of 6%-8% in the decade up to 2012, one of Africa's strongest performances. Mozambique's ability to attract large investment projects in natural resources is expected to fuel continued high growth in coming years. Revenues from these vast resources, including natural gas, coal, titanium and hydroelectric capacity, could overtake donor assistance within five years.GDP (purchasing power parity):$26.69 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 119$24.83 billion (2011 est.)$23.13 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$14.6 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:7.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 237.3% (2011 est.)7.1% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$1,200 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 210$1,100 (2011 est.)$1,100 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:0% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1425.2% of GDP (2011 est.)4.8% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 77.3%government consumption: 13.5%investment in fixed capital: 24.8%investment in inventories: 0.9%exports of goods and services: 27%imports of goods and services: -43.8%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 29.5%industry: 23.9%services: 46.5% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:cotton, cashew nuts, sugarcane, tea, cassava (tapioca), corn, coconuts, sisal, citrus and tropical fruits, potatoes, sunflowers; beef, poultryIndustries:aluminum, petroleum products, chemicals (fertilizer, soap, paints), textiles, cement, glass, asbestos, tobacco, food, beveragesIndustrial production growth rate:12% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 6Labor force:10.1 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 81%industry: 6%services: 13% (1997 est.)Unemployment rate:17% (2007 est.)country comparison to the world: 15221% (1997 est.)Population below poverty line:52% (2009 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 1.9%highest 10%: 36.7% (2008)Distribution of family income - Gini index:45.6 (2008)country comparison to the world: 3747.3 (2002)Budget:revenues: $4.315 billionexpenditures: $4.904 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:29.6% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 94Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-4% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 142Public debt:34.6% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 10634.5% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):2.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 4310.4% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:9.5% (17 January 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1003.25% (31 December 2010 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:16.81% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1819.1% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$4.335 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 102$3.574 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$5.268 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 128$4.095 billion (31 December 2010 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$3.9 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 126$3.392 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$NACurrent account balance:-$2.432 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 144-$1.615 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$3.469 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 126$3.118 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:aluminum, prawns, cashews, cotton, sugar, citrus, timber; bulk electricityExports - partners:South Africa 30.9%, Belgium 12.8%, China 9%, Italy 7.8%, Spain 6.2%, India 5.6% (2012)Imports:$6.167 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 120$5.368 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and equipment, vehicles, fuel, chemicals, metal products, foodstuffs, textilesImports - partners:South Africa 30.7%, China 12.2%, India 11.4%, US 5.1%, Portugal 4.8%, Australia 4.4% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$2.77 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 113$2.469 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$4.562 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 122$4.097 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:meticais (MZM) per US dollar -28.383 (2012 est.)29.075 (2011 est.)33.96 (2010 est.)26.28 (2009)24.125 (2008)Energy ::MozambiqueElectricity - production:14.83 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Electricity - consumption:10.19 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Electricity - exports:9.462 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 21Electricity - imports:8.537 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Electricity - installed generating capacity:2.28 million kW (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 98Electricity - from fossil fuels:0.1% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 206Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:99.9% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Electricity - from other renewable sources:0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 163Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 169Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 156Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 102Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 210Refined petroleum products - consumption:19,580 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 128Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 204Refined petroleum products - imports:13,200 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 123Natural gas - production:3.12 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 54Natural gas - consumption:80 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 107Natural gas - exports:3.04 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 101Natural gas - proved reserves:127.4 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 51Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:2.728 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 143Communications ::MozambiqueTelephones - main lines in use:88,100 (2011)country comparison to the world: 147Telephones - mobile cellular:7.855 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 89Telephone system:general assessment: a fair telecommunications system that is shackled with a heavy state presence, lack of competition, and high operating costs and chargesdomestic: stagnation in the fixed-line network contrasts with rapid growth in the mobile-cellular network; mobile-cellular coverage now includes all the main cities and key roads, including those from Maputo to the South African and Swaziland borders, the national highway through Gaza and Inhambane provinces, the Beira corridor, and from Nampula to Nacala; extremely low fixed-line teledensity; despite significant growth in mobile-cellular services, teledensity remains low at about 35 per 100 personsinternational: country code - 258; landing point for the EASSy and SEACOM fiber-optic submarine cable systems; satellite earth stations - 5 Intelsat (2 Atlantic Ocean and 3 Indian Ocean) (2011)Broadcast media:1 state-run TV station supplemented by private TV station; Portuguese state TV's African service, RTP Africa, and Brazilian-owned TV Miramar are available; state-run radio provides nearly 100% territorial coverage and broadcasts in multiple languages; a number of privately owned and community-operated stations; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters are available (2007)Internet country code:.mzInternet hosts:89,737 (2012)country comparison to the world: 82Internet users:613,600 (2009)country comparison to the world: 113Transportation ::MozambiqueAirports:98 (2013)country comparison to the world: 57Airports - with paved runways:total: 21over 3,047 m: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 9914 to 1,523 m: 5under 914 m: 4 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 772,438 to 3,047 m: 11,524 to 2,437 m: 9914 to 1,523 m: 29under 914 m:38 (2013)Pipelines:gas 972 km; refined products 278 km (2013)Railways:total: 4,787 kmcountry comparison to the world: 38narrow gauge: 4,787 km 1.067-m gauge (2008)Roadways:total: 30,331 kmcountry comparison to the world: 96paved: 6,303 kmunpaved: 24,028 km (2000)Waterways:460 km (Zambezi River navigable to Tete and along Cahora Bassa Lake) (2010)country comparison to the world: 86Merchant marine:total: 2country comparison to the world: 143by type: cargo 2foreign-owned: 2 (Belgium 2) (2010)Ports and terminals:Beira, Maputo, NacalaMilitary ::MozambiqueMilitary branches:Mozambique Armed Defense Forces (Forcas Armadas de Defesa de Mocambique, FADM): Mozambique Army, Mozambique Navy (Marinha de Guerra de Mocambique, MGM), Mozambique Air Force (Forca Aerea de Mocambique, FAM) (2012)Military service age and obligation:registration for military service is mandatory for all males and females at 18 years of age; 18-35 years of age for selective compulsory military service; 18 years of age for voluntary service; 2-year service obligation; women may serve as officers or enlisted (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 4,613,367 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 2,677,473females age 16-49: 2,941,073 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 274,602female: 280,008 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:0.6% of GDP (2012)country comparison to the world: 158Transnational Issues ::MozambiqueDisputes - international:South Africa has placed military units to assist police operations along the border of Lesotho, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique to control smuggling, poaching, and illegal migrationIllicit drugs:southern African transit point for South Asian hashish and heroin, and South American cocaine probably destined for the European and South African markets; producer of cannabis (for local consumption) and methaqualone (for export to South Africa); corruption and poor regulatory capability make the banking system vulnerable to money laundering, but the lack of a well-developed financial infrastructure limits the country's utility as a money-laundering center"
The World Factbook. 2014.
